Why Toolpad?
Learn how Toolpad approaches building internal tools, and how it can be useful to you.
TL;DR
- Higher-level API. Toolpad operates at a higher abstraction level than Material UI. It sets healthy UI constraints that prevent common pitfalls and anti-patterns.
- Drag-and-drop builder. Toolpad comes with a drag-and-drop builder to simplify UI building. The builder saves the UI as a YAML file, so you can even modify and version the visual output on your file system.
- Less boilerplate so you can focus on the essential parts of the app.
- Run alongside existing code. It integrates well with your existing code. You can use your database models, client libraries, secrets, and bespoke components directly.
- Single source of truth. Because Toolpad runs alongside your existing code, it lets you maintain a single source of truth for all business logic.
- Integrates well with your development lifecycle. Your project lives on your file system. You can use your own IDE, version control system, deployment target, CLI tools.
After reviewing multiple products and approaches, a few recurring areas of concern were noticed. Let's take a closer look at them:
Trade-offs with pro-code tools
Compromised delivery speed
Every organization aims to achieve fast delivery, but in order to accommodate various use cases, developers are often pushed to choose flexible pro-code solutions. However, this flexibility often comes at the cost of speed. Pro-code provides lower-level abstractions for greater control, but as use cases scale, they quickly involve a growing maintenance burden that can't be avoided.
A lot of boilerplate
To connect backend data to the browser and set up data-display components, a substantial amount of boilerplate HTML, CSS, and JavaScript glue code is often required.
Lower-level abstraction
Creating internal tools demands knowledge of a front-end framework. While this aspect might be intriguing to some, most developers of internal tools often consider managing the lower-level APIs, HTML, and CSS as an additional burden.
Trade-offs with low-code tools
There exist many low-code code tools specifically for internal use cases. They offer speed, but come with some trade-offs:
Extensibility
Low-code tools can be hard to extend. When the tool can't handle a particular task by default, integrating your own code seamlessly is often a challenge. This lack of flexibility often results in having to write custom code inside these apps and storing your business logic within their configuration files.
Duplication and fragmentation
When working with external low-code or no-code tools, the duplication of code and logic can frequently occur because of a lack of extensibility. Developers invest valuable time in hunting down specific versions of business logic and maintaining them in multiple places. This lack of a unified reference point within the codebase can compromise its scalability, making maintenance and debugging more challenging.
Loss of control
When developers use external tools, they frequently sacrifice their autonomy and become restricted by the options provided by the tool. The introduction of a black-box element removes control over the entire process, including integrations, deployment, and version control. This can lead to a significant problem when it comes to the long-term maintainability of internal tools, as it becomes challenging to adapt, extend, or customize them to meet evolving needs.
How Toolpad fits in
Addressing the problems mentioned above leads to a better developer experience. Toolpad solves them in the following ways:
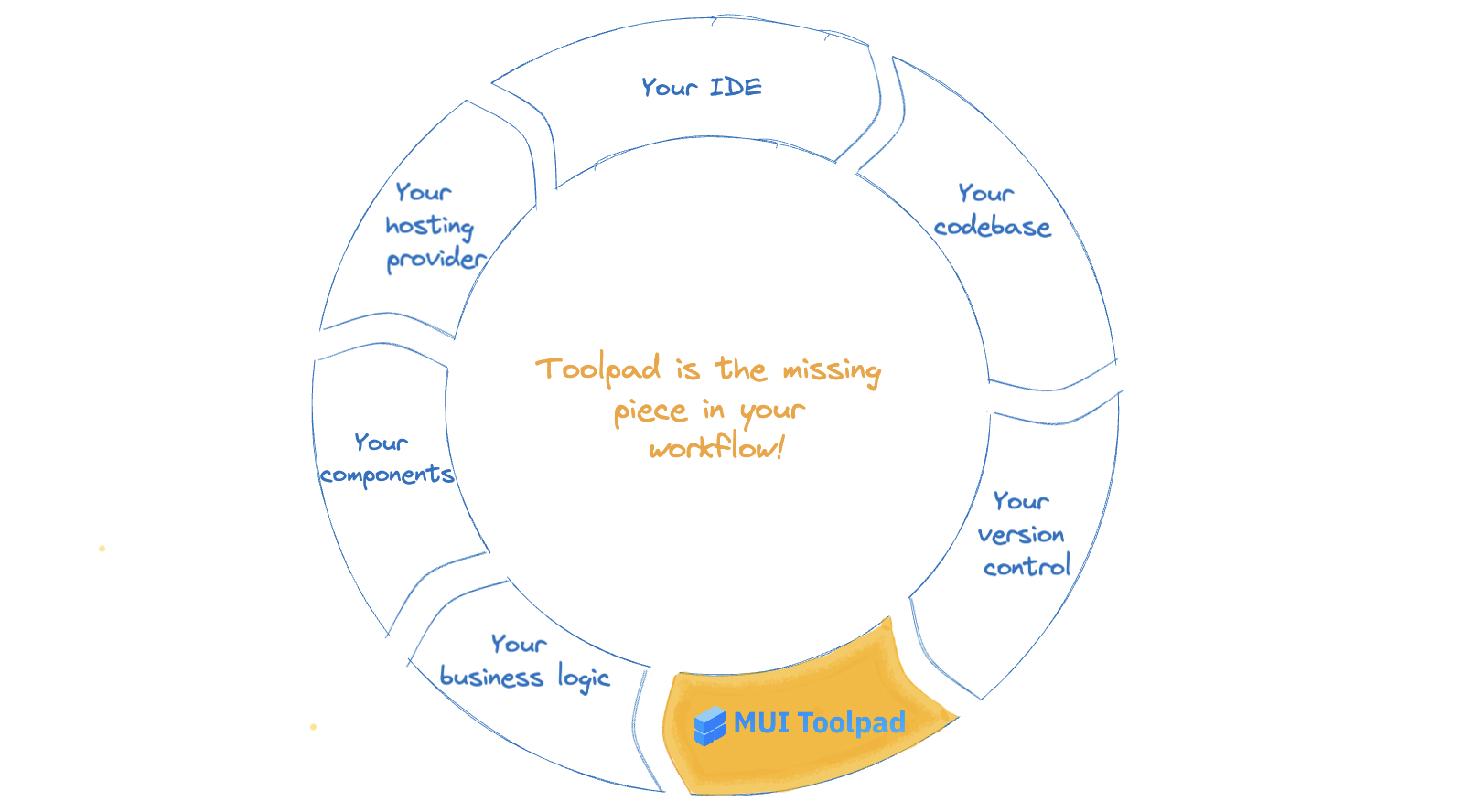
How Toolpad fits in your workflow
Drag-and-drop builder
Toolpad works as a drag-and-drop UI builder and uses MUI's own Material UI components. Material UI includes all of the foundational components required for internal use cases. Toolpad currently supports 16 of them, and we're continuously adding more.
Toolpad supports adding any number of custom React components for other use cases. The drag-and-drop builder enables you to quickly assemble a minimum viable UI that's endlessly customizable, ensuring the best of both worlds: speed and flexibility.
Single source of truth
Toolpad offers two ways to connect to your data, ensuring that you can keep your data in one centralised location and avoid duplicating it for each internal tool you create:
- Link REST APIs to Toolpad through HTTP queries: This common method allows you to access your data directly by building REST queries in a visual interface.
- Write custom functions in your own IDE to connect to any data source: You can use your existing scripts, business logic, database models, client libraries, and secrets. This approach helps you maintain a single, shared data source for all your internal tools, preventing data duplication and ensuring consistency across applications.
Integrates with your development lifecycle
Toolpad empowers you with total control over the entire development lifecycle of your application. It operates on a "local-first" principle, where your project resides on your local file system. This enables you to utilize your preferred Integrated Development Environment (IDE), version control system, deployment target, and Command Line Interface (CLI) tools.
Similar to any Node.js application, you have the flexibility to self-host a Toolpad app on your own server or select a hosting provider that suits your needs, whether it's AWS, Render, Railway, or Heroku. Toolpad does not confine you to its cloud hosting, ensuring you have the freedom to choose the hosting solution that best aligns with your preferences and requirements.
Like any Node.js app, you can self-host a Toolpad app on your own server or any hosting provider of your choice (such as AWS, Render, Railway, or Heroku). Toolpad does not lock you into its cloud hosting.
Seamless collaboration
The Toolpad application configuration is saved in YAML files, which can be conveniently added to Git or any preferred version control tool for collaborative maintenance. Maintaining a private code repository is a fundamental practice for enhancing the security of user data. This eliminates the need to create new collaboration mechanisms for engineers, as the existing tools can be effectively leveraged.
Trust and Safety
While organizations make every effort to protect highly sensitive data and conduct thorough vendor due diligence and compliance assessments, data breaches continue to be a significant concern. Toolpad ensures that you can maintain control over your data, helping to address this issue.
How is Toolpad different from other tools?
🚧 Work in progress